HIV, atau Human Immunodeficiency Virus, iaitu sejenis virus yang menyerang sistem imun tubuh manusia. Sistem imun merupakan barisan pertahanan badan terhadap bakteria, virus, serta jangkitan berbahaya lain. Jika HIV tidak dirawat, virus ini akan melemahkan sistem pertahanan tubuh secara perlahan, menyebabkan jangkitan biasa sekalipun boleh menjadi serius atau mengancam nyawa
Jika tidak dikawal, HIV akhirnya boleh berkembang menjadi AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), iaitu tahap paling teruk bagi jangkitan HIV. Namun begitu, tidak semua pesakit HIV akan menghidap AIDS, terutamanya jika rawatan awal dimulakan.
Hari ini, dengan kemajuan rawatan moden, HIV kini bukan lagi penyakit yang membawa maut. Dengan penjagaan dan rawatan yang sesuai, pesakit HIV mampu menjalani kehidupan yang panjang, sihat dan produktif.
Di Malaysia, masih ramai yang enggan menjalani ujian HIV di Malaysia kerana stigma dan ketakutan. Hakikatnya, HIV boleh menjangkiti sesiapa sahaja tanpa mengira jantina atau latar belakang. Pengesanan awal adalah kunci kepada rawatan yang berjaya dan kualiti hidup yang lebih baik.
Di He Medical Clinic, kami menawarkan secara sulit dan terjamin perkhidmatan ujian HIV di Malaysia dalam suasana yang profesional dan tanpa sebarang prasangka. Sama ada anda berisiko atau sekadar inginkan ketenangan fikiran, kami sedia membantu.
Apa Kesan HIV Terhadap Tubuh Badan?
HIV menyerang sistem imun, iaitu sistem pertahanan semula jadi badan terhadap jangkitan dan penyakit. Secara khususnya, HIV menyerang sejenis sel darah putih yang dikenali sebagai sel CD4 atau T-helper cells. Sel ini amat penting untuk membantu tubuh melawan jangkitan.
Bagaimana Sistem Imun Terjejas?
Sebaik sahaja HIV memasuki tubuh, ia akan mula membiak dengan cepat dan melekat pada sel CD4. Lama-kelamaan, ia akan memusnahkan sel-sel ini. Apabila jumlah sel CD4 menurun, sistem imun menjadi semakin lemah dan tidak mampu melawan bakteria, virus dan juga jangkitan biasa seperti selesema.
Proses ini berlaku secara perlahan. HIV boleh hidup dalam badan selama bertahun-tahun tanpa menunjukkan gejala yang serius. Inilah sebab mengapa ramai yang tidak menyedari bahawa mereka telah dijangkiti sehingga penyakit menjadi lebih teruk.
Apabila kiraan CD4 jatuh di bawah tahap tertentu (biasanya kurang daripada 200 sel per milimeter padu darah), seseorang dianggap telah memasuki tahap AIDS, iaitu peringkat terakhir dan paling berbahaya dalam jangkitan HIV.
Apa Berlaku Jika HIV Tidak Dirawat?
Sekiranya HIV tidak dirawat, sistem imun akan terus merosot. Ini menyebabkan tubuh terdedah kepada apa yang dipanggil "jangkitan oportunistik", iaitu jangkitan yang biasanya mudah ditangkis oleh badan sihat seperti:
- Tuberkulosis (TB)
- Jangkitan kulat
- Radang paru-paru (pneumonia)
- Beberapa jenis kanser seperti Kaposi Sarcoma, limfoma B-sel agresif, dan kanser serviks invasif
Namun begitu, terapi antiretroviral (ART) yang moden mampu menghalang perkembangan ini. Rawatan ART membantu mengawal virus dalam badan, sekaligus mengekalkan kekuatan sistem imun dan mencegah komplikasi.
Jika anda aktif secara seksual atau tergolong dalam kumpulan berisiko tinggi, anda sangat digalakkan untuk menjalani saringan penyakit jangkitan seksual (STD) di He Medical Clinic bagi mengesan HIV dan penyakit lain pada peringkat awal.
Bagaimana HIV Menular?
Menurut kepada Pertubuhan Kesihatan Sedunia (WHO) , HIV biasanya menular melalui cecair badan tertentu seperti darah, air mani, cecair faraj, cecair rektum, dan susu ibuUntuk seseorang dijangkiti, cecair ini perlu masuk ke dalam tubuh melalui membran mukosa (seperti di kawasan kemaluan atau rektum), tisu yang rosak, atau melalui suntikan ke dalam aliran darah.
Cara Utama HIV Berjangkit

- Hubungan Seks Tanpa Perlindungan: Ini merupakan kaedah penularan paling umum, terutamanya melalui seks faraj atau seks dubur tanpa penggunaan kondom. Virus boleh memasuki tubuh melalui luka kecil pada tisu mukosa yang tidak dapat dilihat dengan mata kasar.
- Perkongsian Jarum atau Suntikan: Individu yang berkongsi jarum suntikan sama ada untuk penggunaan dadah atau prosedur lain, berisiko tinggi kerana HIV boleh menular melalui darah yang tercemar.

- Jangkitan dari Ibu kepada AnakSeorang ibu yang hidup dengan HIV boleh menyebarkan virus kepada bayinya semasa kehamilan, proses kelahiran, atau melalui penyusuan susu ibu. Terutamanya jika dia tidak menjalani rawatan.

- Pemindahan Darah (Jarang Berlaku): Di Malaysia, semua darah yang didermakan akan disaring untuk HIV. Namun, di negara atau kawasan yang tidak mempunyai sistem saringan yang baik, ia masih merupakan risiko.
Mitos dan Salah Faham Tentang Cara Penularan HIV Not Transmitted
Masih ramai yang keliru tentang bagaimana HIV disebarkan. Berikut antara salah faham yang biasa berlaku:
- Ciuman atau Pelukan: HIV tidak merebak melalui air liur. Oleh itu, ciuman dan pelukan adalah selamat.
- Berkongsi Peralatan Makan, Tandas, atau Bilik Mandi: Virus HIV tidak boleh hidup lama di permukaan luar dan tidak menular melalui objek harian.
- Gigitan Nyamuk atau Serangga: Berlawanan dengan kepercayaan umum, nyamuk tidak menyebarkan HIV. Virus ini tidak boleh hidup di dalam tubuh serangga dan tidak boleh dipindahkan kepada manusia melalui gigitan.
Bolehkah Kita Dijangkiti HIV Tanpa Melalui Hubungan Seksual?
Ya. Walaupun hubungan seksual tanpa perlindungan adalah penyebab utama jangkitan HIV, terdapat juga cara jangkitan yang tidak melibatkan seksual seperti Perkongsian jarum suntikan, Terdedah kepada darah tercemar, atau Jangkitan dari ibu kepada anak semasa kehamilan atau penyusuan juga boleh menyebabkan jangkitan. Malah, individu yang tidak pernah melakukan hubungan seks juga berisiko sekiranya terdedah melalui saluran-saluran ini.
Apakah Tanda Awal Jangkitan HIV?
Ujian Tanda pertama jangkitan HIV selalunya disalah anggap sebagai demam selsema biasa. Dalam tempoh antara dua hingga empat minggu selepas dijangkiti, ramai individu mengalami satu set gejala yang dikenali sebagai Sindrom Retroviral Akut (ARS) atau Jangkitan HIV Primer. Ini adalah tindak balas semula jadi badan terhadap kehadiran virus dan sering menjadi petanda awal bahawa sesuatu tidak kena.
Gejala Awal HIV yang Menyerupai Selesema
Antara gejala awal HIV yang biasa dialami termasuk:
- Demam
- Sakit tekak
- Keletihan dan sakit-sakit badan
- Kelenjar limfa bengkak
- Ruam pada kulit (hiv rash), lazimnya muncul di bahagian atas badan seperti dada atau belakang, dan mungkin juga di muka
Gejala-gejala ini biasanya berlarutan selama beberapa hari hingga beberapa minggu dan kemudian akan hilang sendiri, tetapi virus masih kekal dalam tubuh badan. Inilah sebab ramai yang tidak menyedari bahawa mereka telah dijangkiti, melainkan jika mereka menjalani ujian HIV.
Pada peringkat awal jangkitan, HIV adalah paling mudah merebak kerana virus ini sedang membiak dengan pantas dalam tubuh badan. Jika anda baru-baru ini melakukan hubungan seks tanpa perlindungan, berkongsi jarum suntikan, atau merasakan diri mungkin terdedah kepada HIV dan kini mengalami simptom tertentu, segeralah dapatkan ujian saringan.
Gejala HIV Dalam Kalangan Lelaki: Apa Yang Perlu Diperhatikan?
Walaupun gejala HIV boleh berlaku pada lelaki dan wanita, terdapat beberapa tanda khusus untuk kalangan lelaki yang sering terlepas pandang atau disalah tafsir. Memahami gejala awal ini amat penting bagi memastikan ujian dan rawatan dapat dimulakan seawal mungkin.
1. Penurunan Nafsu Seks atau Masalah Ereksi

Antara simptom yang paling kerap dilaporkan oleh pesakit lelaki ialah hilang keinginan seksual atau atau kesukaran mendapatkan atau mengekalkan ereksi. Ini boleh disebabkan oleh perubahan hormon atau kelelahan yang kronik akibat sistem imun yang mula terjejas.
Jika anda mengalami mati pucuk Ia mungkin menjadi petanda awal jangkitan HIV atau masalah kesihatan lain yang lebih serius. Ketahui lebih lanjut mengenai mati pucuk dan puncanya di sini.
Ruam Pada Bahagian Atas Badan (HIV rash)
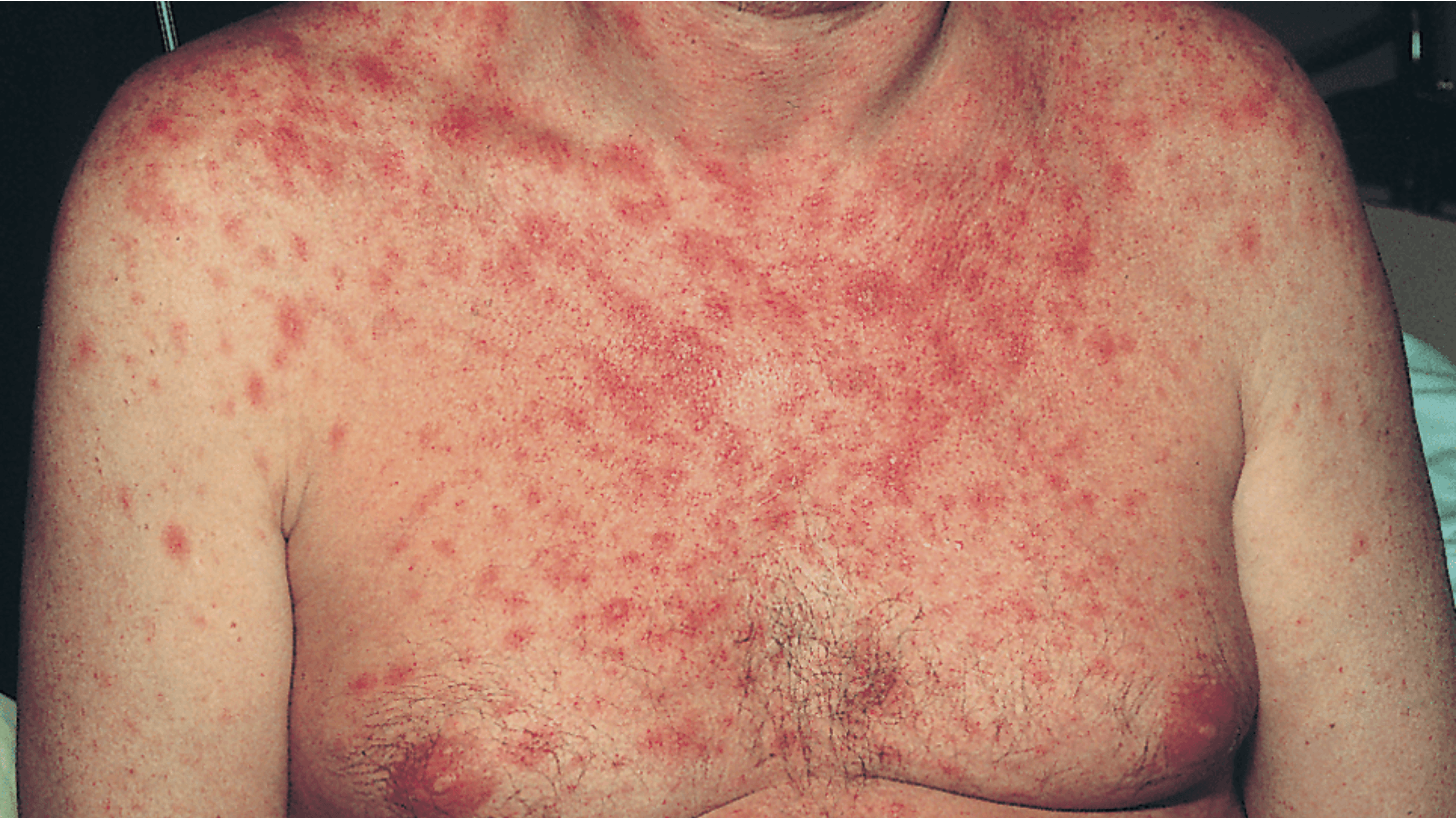
Ujian ruam merah rata yang kelihatan di dada, belakang atau muka. Ruam ini tidak gatal dan boleh muncul secara tiba-tiba. Ia sering berlaku seiring dengan demam dan rasa lemah badan. Ruam ini adalah tindak balas badan terhadap jangkitan virus pada peringkat awal dan merupakan petunjuk penting kepada acute HIV infection.
3. Sering Berpeluh Pada Waktu Malam

Jika anda kerap bangun tengah malam dengan pakaian dan cadar basah tanpa sebab yang jelas, ini mungkin salah satu tanda HIV. Peluh malam yang berlebihan, walaupun dalam bilik berhawa dingin, boleh berlaku pada peringkat awal dan berterusan dalam jangkitan HIV kronik.
4. Kelenjar Limfa Bengkak
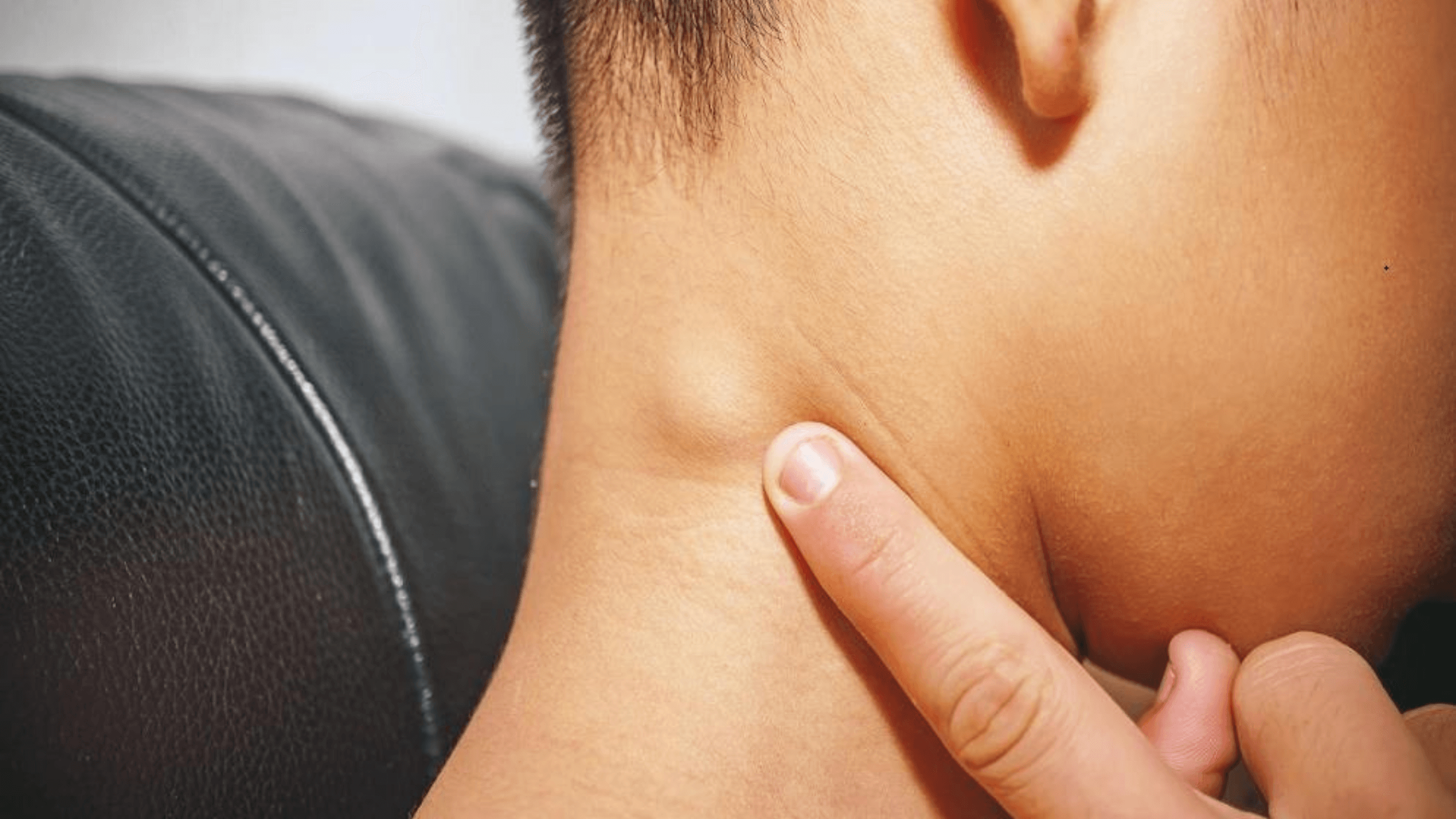
Virus HIV memberi kesan langsung kepada sistem limfa. Oleh itu, kelenjar limfa yang membengkak,terutama di bahagian leher, ketiak, atau celah paha, merupakan antara tanda awal jangkitan. Bengkak ini biasanya tidak menyakitkan, tetapi jelas dan berlarutan.
5. Kehilangan Berat Badan Secara Mendadak

Kehilangan berat badan secara tiba-tiba (lebih 10%) daripada berat asal tanpa sebarang usaha, boleh menjadi tanda HIV sedang melemahkan tubuh. Gejala ini dikenali sebagai HIV wasting syndrome dan lebih ketara dalam peringkat lanjut, tetapi juga boleh bermula sejak awal, terutama dalam kalangan lelaki yang tidak menyedari status jangkitan mereka.
Adakah HIV Boleh Disembuhkan?
Buat masa ini , belum ada penawar sepenuhnya untuk HIV. Namun begitu, berita baiknya ialah terdapat rawatan yang sangat berkesan, yang membolehkan individu yang hidup dengan HIV menjalani kehidupan panjang, sihat dan berkualiti tinggi.
Apakah Rawatan Yang Tersedia Untuk HIV?
Rawatan utama bagi HIV dikenali sebagai Terapi Antiretroviral (ART).Ia melibatkan gabungan ubat-ubatan yang:
- Mengurangkan jumlah virus dalam badan (viral load)
- Melindungi sistem imun dengan mengekalkan jumlah sel CD4 yang sihat
- Menghalang perkembangan kepada AIDS
- Mengurangkan risiko penyebaran HIV kepada orang lain
Apabila diambil setiap hari seperti yang disarankan, ART mampu menurunkan virus ke tahap tidak dapat dikesan (undetectable).Ini bermakna virus berada pada tahap yang terlalu rendah untuk dikesan dalam ujian makmal biasa, dan paling penting ia tidak dapat dipindahkan kepada pasangan melalui hubungan seksual..
Mengapa Belum Ada Penawar HIV?
HIV mempunyai kebolehan unik untuk menyerap masuk ke dalam DNA sel imun, menjadikannya sangat sukar untuk dihapuskan sepenuhnya. Para penyelidik di seluruh dunia sedang giat mencari penawar, dan terdapat beberapa kes eksperimen yang berjaya. Contohnya melalui pemindahan sumsum tulang, tetapi ia hanya sesuai dalam kes-kes perubatan yang sangat khusus dan tidak boleh digunakan secara umum.
Cara Melindungi Diri Daripada HIV
HIV boleh dicegah. Pencegahan bermula dengan kesedaran dan tindakan yang bertanggungjawab. Sama ada anda aktif secara seksual atau tidak, memahami bagaimana virus ini menular adalah langkah pertama untuk melindungi diri dan pasangan anda.
Pengesanan Awal Boleh Mengubah Segalanya
Memulakan rawatan ART pada peringkat awal amatlah penting kerana Ia membolehkan sistem imun anda pulih, mengurangkan komplikasi, dan melindungi pasangan anda. Semakin lama anda menangguhkan rawatan, semakin banyak kerosakan yang boleh dilakukan oleh HIV secara senyap terhadap tubuh anda.
Di He Medical Clinic, kami menyediakan perkhidmatan ujian HIV yang mampu milik dan sulit di Malaysia, diikuti dengan rujukan rawatan yang sesuai serta sokongan berterusan kerana kami percaya bahawa pengurusan HIV harus bermula dengan belas ihsan dan jawapan yang jelas.
Amalkan Seks Selamat
Penggunaan kondom dengan betul semasa hubungan seks adalah cara paling berkesan untuk mencegah HIV. Kondom bertindak sebagai penghalang kepada cecair badan yang boleh membawa virus HIV. Penggunaan kondom juga penting walaupun dalam hubungan monogami, terutamanya jika pasangan pernah mempunyai pasangan seksual sebelum ini.
Pertimbangkan PrEP dan PEP
Jika anda tergolong dalam kumpulan berisiko tinggi, Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) boleh mengurangkan risiko jangkitan HIV sehingga 99%. Ia merupakan pil harian yang mencegah jangkitan jika virus memasuki tubuh. Manakala Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) pula ialah ubat kecemasan yang perlu diambil dalam masa 72 jam selepas terdedah kepada HIV, contohnya melalui hubungan tanpa perlindungan atau jarum tercemar. Kedua-dua rawatan ini hanya boleh diperoleh melalui nasihat doktor.
Lakukan Ujian HIV Secara Berkala
Ramai pesakit HIV tidak menunjukkan gejala pada peringkat awal. Ujian HIV secara berkala membolehkan pengesanan awal dan rawatan segera. Langkah ini dapat memberi kesedaran terhadap status diri dan membolehkan anda membuat keputusan kesihatan yang lebih baik untuk mencegah komplikasi jangka panjang.
Elakkan Perkongsian Jarum
Jika anda menggunakan dadah suntikan, pastikan anda menggunakan peralatan yang bersih dan steril setiap kali. Perkongsian jarum adalah antara kaedah penularan HIV yang paling berisiko tinggi.
Kurangkan Bilangan Pasangan Seksual
Semakin ramai pasangan seksual, semakin tinggi risiko jangkitan. Hubungan monogami dengan pasangan yang telah diuji dan negatif HIV adalah langkah pencegahan terbaik.
Soalan Lazim Mengenai HIV (FAQ)
Tidak.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) ialah virus yang menyerang sistem imun manusia. AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) pula ialah tahap akhir jangkitan HIV, di mana sistem imun menjadi sangat lemah, menyebabkan tubuh mudah dijangkiti penyakit serius atau kanser.
Dengan rawatan yang betul, ramai individu dengan HIV tidak menghidap AIDS.
Dengan kemajuan perubatan moden, individu yang hidup dengan HIV boleh menjalani hayat yang hampir sama panjang dengan individu tanpa HIV, terutamanya jika didiagnosis awal dan dirawat secara konsisten. Terapi Antiretroviral (ART) membantu mengawal virus, mengelak komplikasi dan memanjangkan jangka hayat. Ramai pesakit HIV kini hidup sihat hingga umur 70 tahun dan ke atas.
Sudah tentu.
Individu dengan HIV boleh berkahwin, menjalani hubungan yang sihat dan bahkan mempunyai anak bebas HIVDengan rawatan yang betul, jumlah virus boleh diturunkan ke tahap tidak dapat dikesan, sekali gus tidak boleh ditularkan kepada pasangan.Terdapat juga kaedah perubatan yang selamat untuk hamil tanpa mendedahkan pasangan atau bayi kepada risiko jangkitan.
Pesakit HIV masih boleh hidup seperti orang lain, tetapi perlu mengambil langkah berjaga-jaga seperti::
- Jangan kongsi jarum atau barangan peribadi yang mungkin tercemar dengan darah
- Amalkan seks selamat setiap masa
- Jangan tinggalkan ubat tanpa arahan doktor kerana ia boleh menyebabkan virus HIV menjadi kebal
- Hadkan pengambilan alkohol atau dadah, yang boleh mengganggu keberkesanan rawatan
Selain itu, individu dengan HIV boleh bekerja, melancong, bersenam, berkahwin, dan membina keluarga seperti orang lain.
Berita baiknya , HIV bukan lagi hukuman mati. Kini:
- HIV boleh dikawal ke tahap tidak dapat dikesan
- Pesakit boleh hidup sihat, aktif dan normal
- Virus tidak boleh ditularkan apabila viral load berada pada tahap tidak dapat dikesan
- Pencegahan seperti PrEP HIV melindungi pasangan bebas HIV
- Ujian awal dan rawatan awal membawa kepada hasil kesihatan yang jauh lebih baik
Lagi awal seseorang membuat diagnosis, lebih besar peluang untuk kekal sihat sepanjang hayat.
Ya. Dengan rawatan yang betul, individu dengan HIV boleh menjalani kehidupan biasa dengan jangka hayat yang panjang dan kualiti hidup yang tinggi. Ubat moden boleh menurunkan tahap virus ke paras tidak dapat dikesan, yang bermaksud ia tidak boleh disebarkan kepada orang lain.
Lakukan Ujian HIV Hari Ini – Kekal Maklum, Kekal Selamat
Di He Medical Clinic, kami komited untuk menyediakan perkhidmatan ujian HIV yang, dan cepat, sulit dan tidak prejudis . Sama ada anda mengalami gejala, pernah terdedah kepada risiko, atau sekadar mahukan kepastian, kami sedia membantu anda dari awal hingga akhir.
Jadi buatlah temu janji dengan He Medical Clinic untuk ujian HIV yang profesional, sulit dan menyeluruh. Anda akan dapat maklumat yang jelas, rawatan yang berkesan dan sokongan berterusan.